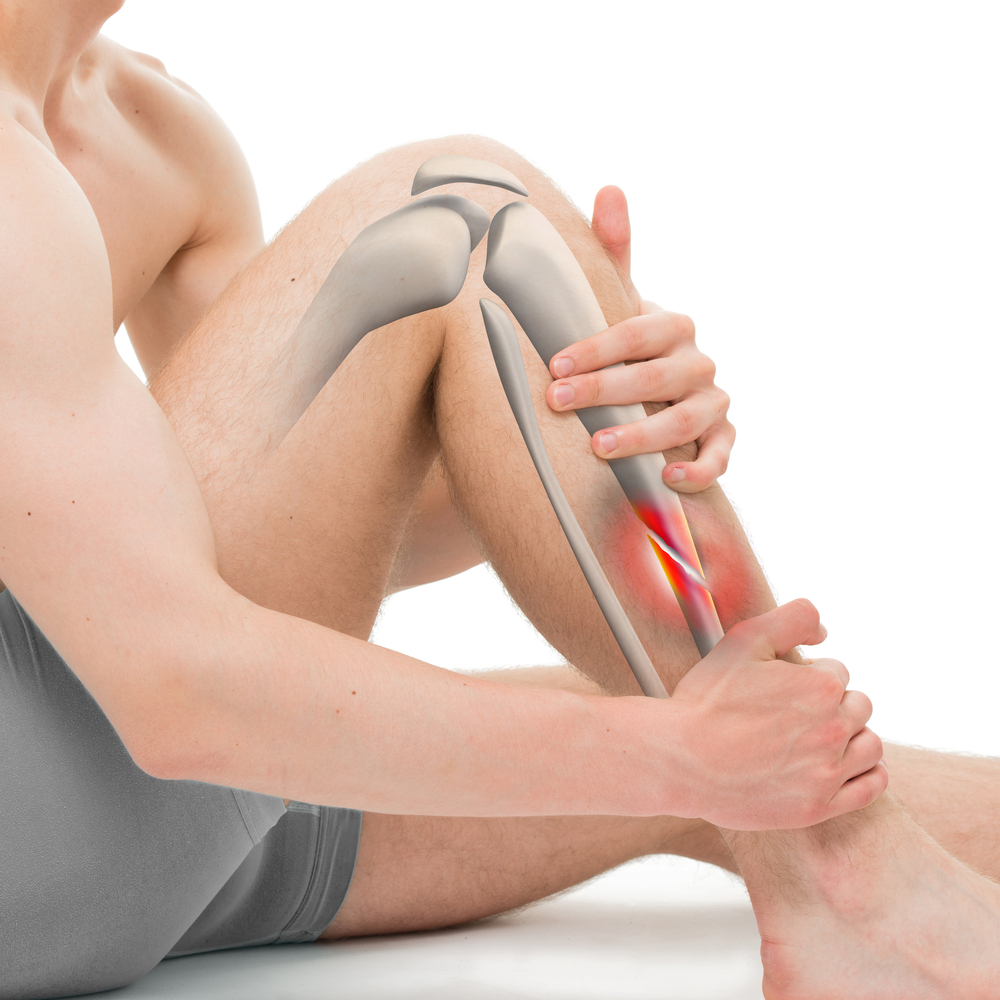
A tibia fracture, also known as a shinbone fracture, occurs when there is a break in the larger of the two bones in the lower leg. This type of fracture can happen due to various reasons, including trauma from falls, sports injuries, or motor vehicle accidents. The severity of tibia fractures can vary, ranging from hairline fractures to complex breaks that puncture the skin (open fractures). Common symptoms include severe pain, swelling, bruising, inability to bear weight on the affected leg, and visible deformity in severe cases. Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, X-rays, and sometimes additional imaging tests like CT scans to assess the extent and severity of the fracture.
Treatment depends on the type and severity of the fracture but may include immobilization with a cast or brace, realignment of the bones (reduction) if necessary, and surgical intervention with internal fixation (such as plates, screws, or rods) to stabilize the bones and promote proper healing. Rehabilitation, including physical therapy, is often essential to restore strength, mobility, and function to the affected leg after the fracture has healed. Prompt and appropriate treatment is crucial to minimize complications and optimize recovery outcomes for individuals with tibia fractures.
